Dexter Thillen, senior ICT analyst at BMI and part of technology, media, and telecom (TMT) team, contributed to this report and found three key megatrends:
• IoT and big data: the main megatrends
• The disruptive impact of AI, blockchain and quantum computing
• Telecoms operators focusing on services and content
Cybersecurity, while not a megatrend, is also a key element of BMI thinking, as it will have an impact across all industries. As well as the report, BMI conducted a survey of 250 senior executives across various sectors and countries. From this BMI highlighted the key results, showing how prepared the telecoms industry is for these upcoming trends as it is uniquely placed, being both a provider and a user of these new technologies.
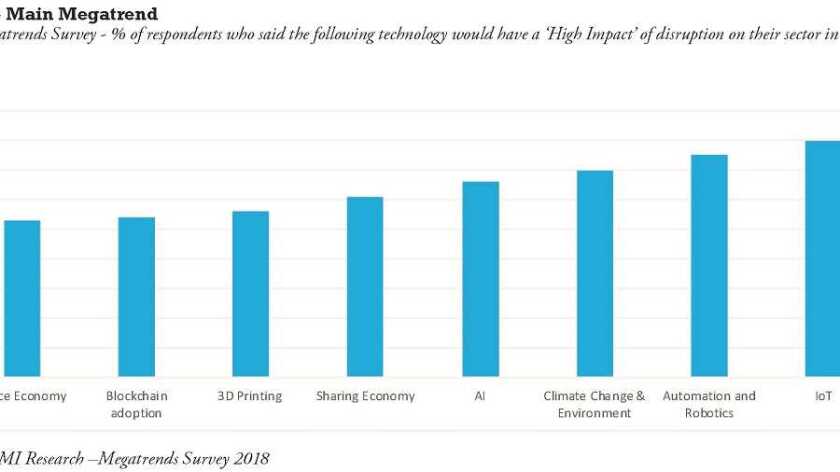
Looking across the different industries, it is clear that the IoT is seen as having the most disruptive impact, with a score of 80%. Automation/robotics, and climate change, follow with 75% and 70% respectively, while other technologies, such as AI and blockchain, are further behind, with scores of 66% and 54% respectively.
The IoT is global and not a tech-specific trend and, while operators are strongly positioned to take advantage, they also need to realise they require partnerships to offer the best possible service. Operators can be the main interlocutor to the end-user, but they need others to meet the specific demand from other industries.
Looking at respondents from the TMT sector only, IoT is also a key trend, as it will be used to improve internal processes and lower costs as well as a new product to external clients.
BMI found 89% of respondents believe it will have a high impact in the next five years, dropping to 84% in the next 30, and this matches the current investment cycle, with 78% of respondents saying that the IoT was one of the main areas of current spending. AI is also an area of investment, with 73% of respondents saying it was a current area of spending, but over a longer timeline than IoT concerning its impact.
Only 65% of respondents said they would have a high impact in the next five years, which increases to 76% in the next 30 years.
AI will have a key role with the development of software-enabled solutions into the network, such as SDN or NFV, while standards for 5G will include the use of machine learning.
The survey highlights that the biggest impact from IoT, automation and big data will be in terms of cost reduction and additional revenue streams, with respective average scores of 69.4% and 64.9%.
BMI has long held the view that technology is first used for cost savings, so that companies can find higher margins in markets where revenues are stagnant, with the second stage being to use these technologies to create new revenue streams, through an evolution of their business model. This is also why enterprises will be the first to adopt new technologies, before moving into the mass-market consumer space.
The survey also shows that only 68% of respondents are investing heavily into the personalisation of services: BMI expected more. The ability of technology to switch from a product to a service will be a key element of any updated business model. Also for telecoms operators it is important to realise that connectivity, while important, is not enough. Personalisation will act as a key differentiator for operators but this also requires a change of mind-set and a shift in culture to meet these new challenges.
Cybersecurity is another key area of investment according to 76% of respondents, and 84% believe that the TMT sector is well prepared to deal with cybersecurity issues, second only to the pharmaceutical industry. The TMT sector has more experience than others when dealing with these threats, but optimism should not turn into overconfidence.
Nothing is fully secure, as anything connected can be hacked, with the ubiquitous and interdependence of devices making it a clear risk.
Operators can become key players in the cybersecurity battle, because without trust, none of these technologies will have the impact we all expect.