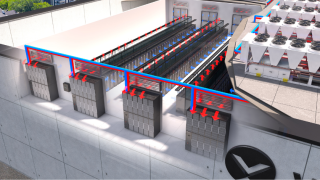
Carried out at the Xi'an Joint Innovation Lab, the group achieved the industry's first sub-band full-duplex gNodeB (gNB), with uplink throughput of over 1.47Gbps and lower end-to-end latency of 3.9 milliseconds simultaneously in Time Division Duplex (TDD) frequency band with 100MHz system bandwidth.
The flexible frame structure was verified using Qualcomm's Snapdragon X65 Modem-RF System, the company's 5G modem-to-antenna solution.
SBFD is a promising enhancement as it allows gNB to perform simultaneous transmission and reception at the same time but in different non-overlapping sub-bands. 5G Advanced SBFD is a key milestone towards full duplex evolution.
With SBFD, gNB allows flexible Upload/Download resource allocation and adaptation based on Upload/Download traffic. it will also help reduce latency while improving Upload coverage and system throughput.
The project marks ZTE's launch of the industry's first SBFD remote radio unit with enhanced transceiver architecture created by integrating multiple self-interference cancellation schemes like spatial isolation, analog sub-band filter and digital interference cancellation.
The self-interference could be mitigated over 130dB which enables optimal reception performance of the uplink signal at the gNB receiver. In addition, ZTE's SBFD solution adopts “Flexible” slot in frame structure configuration and uses User Equipment-level radio resource scheduling mechanisms to be compatible with legacy User Equipment.
In related news, May saw ZTE Corporation together with the Zhejiang Branch of China Telecom, jointly built a self-adaptive spatiotemporal cognitive network.
Using ZTEs Radio Composer, 'spatiotemporal' refers to the network's ability to use intelligent user navigation to match network resources with traffic through on-demand elastic capabilities across its two-layer network.